Otoplasty, big ears operation
Plastic surgery to repair large ears is an operation that consists of shaping the cartilage of the ears and the excess skin until the desired appearance and size is achieved. It is a fairly simple and quick operation to perform, it is not very complicated, and its risk is very low.
Very often minors come to us, accompanied by their parents, because they are not happy with their physical appearance and want to give a solution as soon as possible, since the change in the physiognomy of the face is quite large. It is an intervention whose result is very satisfactory for the patient.
Clínica Sanza in Barcelona, is a reference center in otoplasty surgery.

Book a visit
You can do it in 3 ways:
– Free on-site visit: Call +34 932066540 from Monday to Thursday from 9:00 am to 6:00 pm and Friday from 9:00 am to 3:00 pm.
– Free on-site visit with IMMEDIATE booking: For booking outside office hours. We charge 60 € on your card to avoid false bookings. It is refunded on the day you come to the consultation.
– ONLINE Visit: Video conference using whatsapp or Zoom. Cost of 60 € non-refundable. When booking indicate in the comments that you want videoconferencing and not on-site.

Book a visit
You can do it in 3 ways:
– Free on-site visit: Call +34 932066540 from Monday to Thursday from 9:00 am to 6:00 pm and Friday from 9:00 am to 3:00 pm.
– Free on-site visit with IMMEDIATE booking: For booking outside office hours. We charge 60 € on your card to avoid false bookings. It is refunded on the day you come to the consultation.
– ONLINE Visit: Video conference using whatsapp or Zoom. Cost of 60 € non-refundable. When booking indicate in the comments that you want videoconferencing and not on-site.
WHERE DO WE OPERATE?
At Clínica Sanza we rely on the Sagrat Cor Hospital, part of the Quirónsalud group, to perform our surgical procedures.
Its prestige, facilities, medical and healthcare staff, as well as its technology are a guarantee.
BARCELONA: A HEALTH HUB
Do you want to know why it is worth coming to Barcelona for plastic surgery and why so many people come from abroad?
WE ORGANIZE EVERYTHING FOR YOU
Your trip, your flight, your operation, your transfer and your hotel with our support agency. We work with the best travel agencies worldwide.
PATIENT PROFILE
People with a complex about having so-called protruding ears.
Recommended especially in early ages, when the child has complexes or requests the intervention.
SURGERY PROCEDURE
It is a congenital malformation that, although it does not affect the function of the ear, it is an aesthetic problem that can have social stigmas, since it negatively affects the patient’s self-image, especially in children.
Prominent ears can have various shapes and degrees of distortion that begin to manifest themselves at 6 or 7 years of age, when other body features are not yet formed such as the nose, jaw, cranial size, etc.
That is why we recommend the operation at an early age, when the child has complexes or requests it.
The operation is performed through an incision in the back of the ear, through which the cartilage is molded to achieve the desired aesthetic appearance, both in terms of curvature (protruding ears) and projection (protruding ears).
The scar that remains after surgery is a very thin line perfectly camouflaged in the retroauricular folds and is practically invisible, even if the hair is worn very short or the hair is tied back.
DURATION OF THE OPERATION
- 1 to 2 hours of operation
PROTOCOL
Preoperative
- Evaluation of the area to determine the adequacy of the treatment.
- Follow specific guidelines determined by the doctor
- CBC and tests on cardiac and respiratory status if needed
Anesthesia
- Local or sedation in children
Hospitalization
- Outpatient surgery
Postoperative
- Bandage covering both pinnae
- Bandage removal 24 hours after the operation
- Stitch removal 7 to 10 days after surgery
- Medication if required
- Mandatory revisions a few days, weeks and months after surgery, according to prescription
Convalescence
- Once the bandage is removed, resume normal life except for physical exercise.
- After 3 weeks, it is possible to practice physical exercise.
- Avoid direct exposure of the wound to the sun during this period.
RESULTS OF THE OPERATION
- Very natural and satisfactory
- Improvement of the patient’s psychological profile and self-esteem.
DEGREE OF DIFFICULTY
- Simple operation
LEVEL OF RISK
- Low risk surgery
- Risks inherent to the operation: possible recurrence requiring touch-up if an ear becomes slightly detached.
- Risks of any operation: haemorrhage, infection, impaired healing.
BEFORE/AFTER PHOTOS
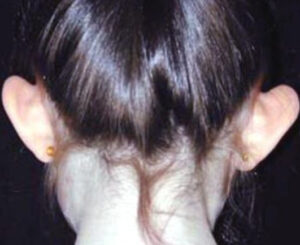
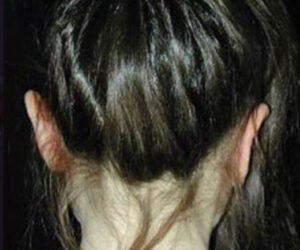
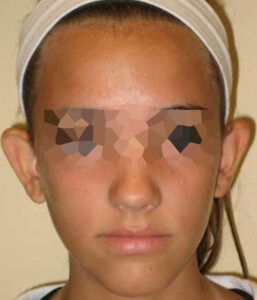
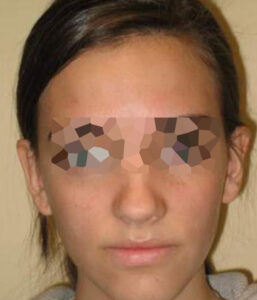
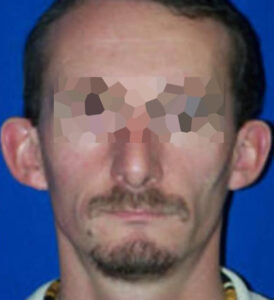
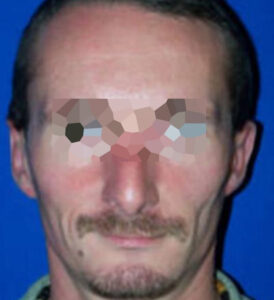
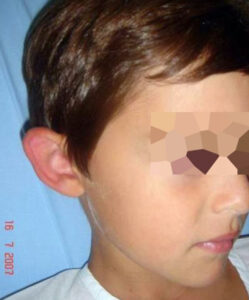
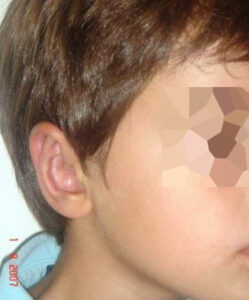
Whatever your case may be, do not hesitate to contact us.
Sanza Clinic in Barcelona, quality of service
Frequently asked questions about big ear surgery
What is the normal size and what is the natural separation of the ears?
The size of the ear is on average 6 cm in height and 3.5 cm in width, with a maximum separation of 2 cm between the auricular cartilage and the head (auriculocephalic angle between 20-30º). Independently everything varies according to related aspects such as head measurements and the size of other facial features, age, sex and height.
What is otoplasty for protruding ears?
Otoplasty of prominent ears is surgery to correct the position of prominent or protruding ears due to the absence of the natural folds of the auricular cartilages (antihelix) or the increased projection of one of them (concha auricularis). Also to reduce the length when they are very long.
Who are the candidates?
Candidates are those patients who wish to improve prominent, cupped or protruding ears, which have an auriculo-cephalic angle greater than 30º and/or project more than 2 cm between the ear cartilage and the head. Everything depends on the individualization of each patient and the affectation that this cosmetic deformity may cause.
What is the ideal age to correct it?
The most advisable age for any operation on the ears is from the moment when the child has practically reached the definitive size of the ears, that is at school age, more or less between 7 or 8 years old. Although the assessment must be individual, that is to say, it may be convenient to advance the operation when the child shows problems with his peers at school. Surgery can also be performed in adults, in fact it is a frequent cause of consultation for complexes brought from childhood.
Is surgery to correct prominent or protruding ears complicated?
It is very simple and can be modified in position, shape and size. Its treatment will depend on the alterations presented by the patient. It is performed with local anesthesia and some sedation on an outpatient basis.
How long does the otoplasty operation take?
Are there visible scars?
The scar to correct prominent ears is hidden in the posterior sulcus, so it is not visible.
What is the procedure like, what type of anesthesia is used?
The procedure to correct protruding ears is performed in the operating room under local anesthesia, with or without sedation, and on an outpatient basis, i.e., it does not require hospitalization.
What are the most frequent complications?
As with any surgical procedure there are risks, but they are very rare and infrequent. The most frequent is the hematoma, which can be visualized in the first 24 hours and easily resolved. Infection so we always prescribe antibiotics to prevent it. In some cases, a recurrence may occur, i.e., some ears may unfold a little. Should this occur it may require some touch-up if necessary after the swelling has passed.
Is the postoperative period very painful and complicated?
The postoperative period during the first 24 hours is not very painful, it is comparable to the discomfort caused by falling asleep for a while on the ear, we place a bandage that we remove the next day of the intervention and then we place an elastic fabric headband, for the next 15 days only to sleep. Recovery is rapid and the patient can resume normal activities almost 4 days after surgery.