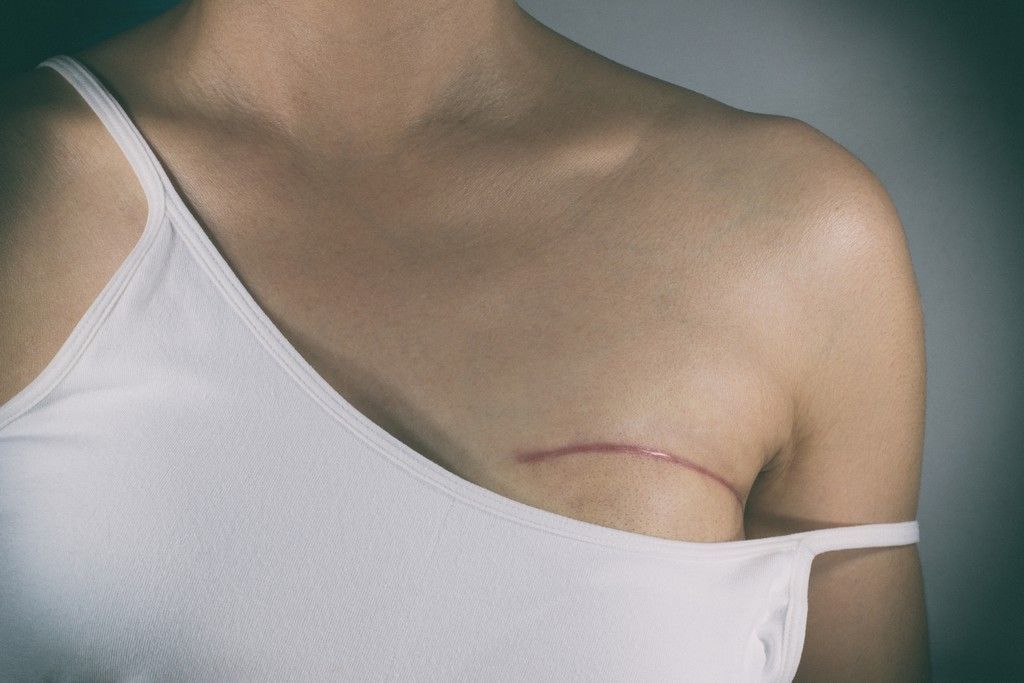
What breast surgery scars look like
All surgeries leave scars that can be more or less visible.
What depends on the visibility of a scar?
It depends on two factors:
- Personal
- Surgeons
Personal factor
Among the personal factors, we can find the skin quality and the way the skin scars. In fact, someone can have a tendency to heal with non-physiological scars, like atrophic scars, hypertrophic or keloids.
Surgeon factor
The other factor depends on the technique used by the surgeon chosen for this intervention, on his/her capacity to disguise the scar in the skin’s natural folds and the type of suture used.
Scar types
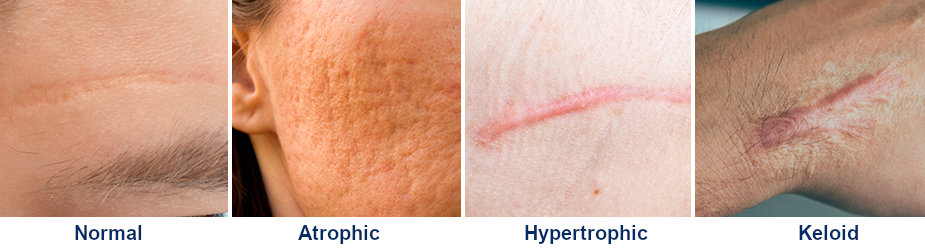
There are 3 different types of scars that we can have. We are going to explain each of them:
1 – Atrophic
This is the development of sparse scar tissue that leads to the wound having a sunken appearance in relation to the surrounding skin. Raised scars may become atrophic as a result of steroid treatment to improve their aesthetic appearance.
2 – Hypertrophic
This is a raised scar, usually darker than the local skin tone or reddish in colour, which is also accompanied by itching.
In this type of lesion, the proliferation of tissue goes beyond the skin surface. Its appearance is related to factors such as stress on the wound and begins to manifest itself from the early stages of repair of the lesion.
3 – Keloids
These are raised scars with a reddish or purple colour due to an excess in the formation of new fibres. These lesions are not related to factors such as stress on the wounds and can appear even several months after the injury occurred.
The difference between a hypertrophic scar and a keloid is that the latter goes beyond the boundaries of the wound and may extend into the surrounding healthy skin. When located near the joints, fibrosis of the skin can result in limitation of joint movements.
Breast augmentation with prosthesis (augmentation mastoplasty)
What are the scars like and where are they located?
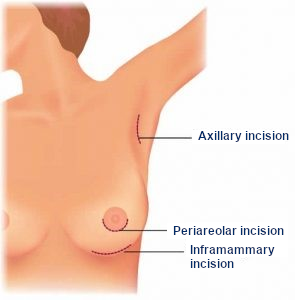
Generally the scars in breast augmentation are quite small, although it depends on the size of the prosthesis chosen.
There can be 4 different scars, depending on where the scar is and what shape it is:
1 – Periareolar
Not very visible and in the lower half of the areola, excellent for small or moderate implants.
2 – Inframammary
Very used, it is easily hidden under the submammary crease with a bra/bikini, great for medium and big prosthesis
3 – Axillary
Less used, due to the risk of infection in the wound as it is in a humid area, it can be used for patients with small breasts or for small or medium implants.
4 – Umbilical way
Used randomly due to the distance between the entrance and the point of destiny, risking a misplacement of the implants, indicated only for saline implants and small ones.
Breast lift (Mastopexy)
What are the scars like and where are they located?
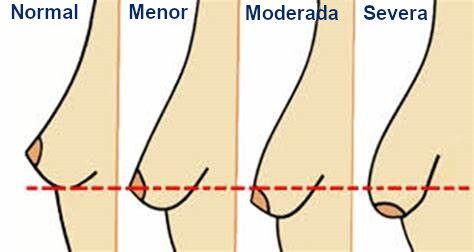
The scars from a breast lift are probably the most feared.
Depending on the size and ptosis level of the breast, the number and shape of scars can change.
Anyhow, you will always have a periareolar scar in the circumference of the nipple.
We can have “I”, “J or L” and “inverted T” scars.
A periareolar scar alone
Can only be done on small breasts and a low ptosis level.
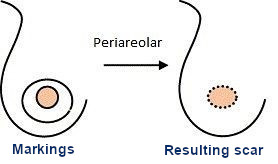
The I-shaped scar (periareolar + vertical)
Can be used for a medium or big breast with a moderate or severe ptosis level. It is the most common scar used at Clínica Sanza, because it leaves less of a marc than with other techniques. Generally, the vertical scar is the one most patients fear, but on the long run it is the one that is less noticeable.
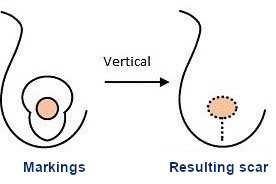
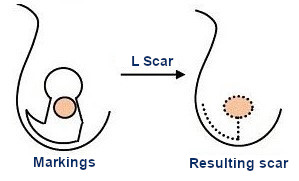
The scar in J or L shape
Is less used, adding to the periearolar there is a vertical scar and a horizontal scar in the middle of the sub mammary fold. It is used for bigger breasts.
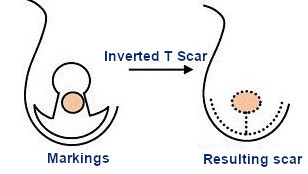
The scar in inverted-T
Is the classic technique, aside from the periareolar scar, there is a vertical scar and one on the sub mammary fold. It is used for very big breasts with a severe ptosis level.
Breast reduction
What are the scars like and where are they located?
The scars from a mammary reduction are identical to those from a breast lift. In this case the technique depends only on the breast size.
How do you take care of wounds?
Surgical wounds in the breast require a healing phase of approximately 15-21 days.
To have an optimised wound and avoid wound dehiscence (stitches opening) and infections, it is necessary to treat them.
- After surgery the wound will be covered with bandages that must not be removed unless your doctor indicates it. The bandage must no be wet under any circumstance so personal hygiene must be done without getting the area wet.
- 3 days after the intervention the wound can be washed unless your doctor indicates the contrary.
- Once the bandage has been removed, you have to check the state the wound is in: if there is a separation from the side, if there is puss, if there is excessive swelling, if the skin is reddened or any other alarming sign, you must set up an appointment or call the emergency number.
- The cleaning of the wound must be done with water and antiseptic liquid soap with soft movements and with no rubbing. Remove the excess soap with a small stream of clean water, saline solution or sterile water over the wound.
- Once the wound is clean, dry it softly with a sterile gauze. Place the iodine solution (Betadine) or ethylic alcohol at 90% over a sterile gauze and apply it over the wound, letting it dry naturally or with a hair dryer using cold air. After that, cover it with a gauze or leave it on the open if your doctor or nurse indicates it.
- Avoid sun exposure during the first 2 months or use a high protection sunblock to avoid the scar to pigment.
- Avoid tension or impacts on the wound; so, you should not do strong efforts with the body parts that have the wound.
- Surgical wounds do not require medication on them unless they are infected. Anyways your doctor would prescribe you the necessary.
- If there is pain, take the painkillers prescribed by your doctor and follow the recommendations.
- If the pain does not stop or increases, go to your check-up or call the emergency phone number.
- It is important to keep a balanced diet or the diet indicated for your case. Vitamin C supplements help a better scarring.
- You must not interrupt any treatment indicated by your doctors (for diabetes, high blood pressure, cholesterol, etc) nor any specific treatment after the surgery without your medical supervision.
- If you have diabetes, it is important to have it under control as a high concentration of glucose (sugar) in blood can complicate the scarring of the wounds.
- It is advisable to reduce alcohol consumption and eliminate smoking as this interferes in the scarring process.
How long are the scars visible and when do they disapear?
Wherever a scalpel passes, there is a scar and the scar is for life.
The process to completely heal lasts approximately one year. The first months, the scars are in a phase called “reactive”, in which they are visibly red, with time, if they are not exposed to the sun, they will clear up. After the fist month more or less, it is recommended to use musk rose oil so they are softer and less visible.